How Calibration Helps the Frozen Food Industry
During the month of March, we celebrate National Frozen Food Month. Giving us the perfect time to delve into this fascinating industry and the many ways it’s benefited our everyday lives.

How Heat, Cold, and Humidity Affect Your Electronic Equipment
The performance of electronic devices must be able to withstand a variety of conditions. In particular, this is true of electronic components used in medical, pharmaceutical, and forensic laboratories, as well as the aerospace and food and beverage industries.
There are a number of ways in which different thermal conditions can affect your electronic devices.

How Frozen Food Became a Giant in The Food Industry
Humans have used the cold to preserve food for centuries, but it wasn’t until 1924 when Clarence Birdseye, an American entrepreneur, made a fascinating discovery that would revolutionize how we preserve fresh food.
Birdseye was fishing in the icy Labrador Territory of Canada and noticed how the fish would freeze almost immediately after pulling them from the water. However, what impressed him the most was that the fish tasted fresh when he thawed them months later.
This event led Clarence Birdseye to find a way to optimize flash freezing for commercial applications. His freezing method prevented the formation of large ice crystals within the food cells, which diminished the product’s taste and changed its texture when thawed.
In time, Birdseye learned to package and flash-freeze food in large quantities making the endeavor commercially viable. Thanks to his vision, more efficient methods of refrigerated transportation followed, creating our modern cold chain logistics that help put food on millions of tables worldwide.
Today’s frozen food industry is a global economic force that continues to grow. Projected industry forecasts estimate that the worldwide market value of frozen foods will reach a staggering 312.3 billion by 2025.
The value of the U.S. frozen food market in 2021 was 55.80 billion. Thanks to consumers’ demand for convenient and cost-effective meal options that require little or no preparation, experts forecast that the industry will grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.7% between 2022 and 2030.
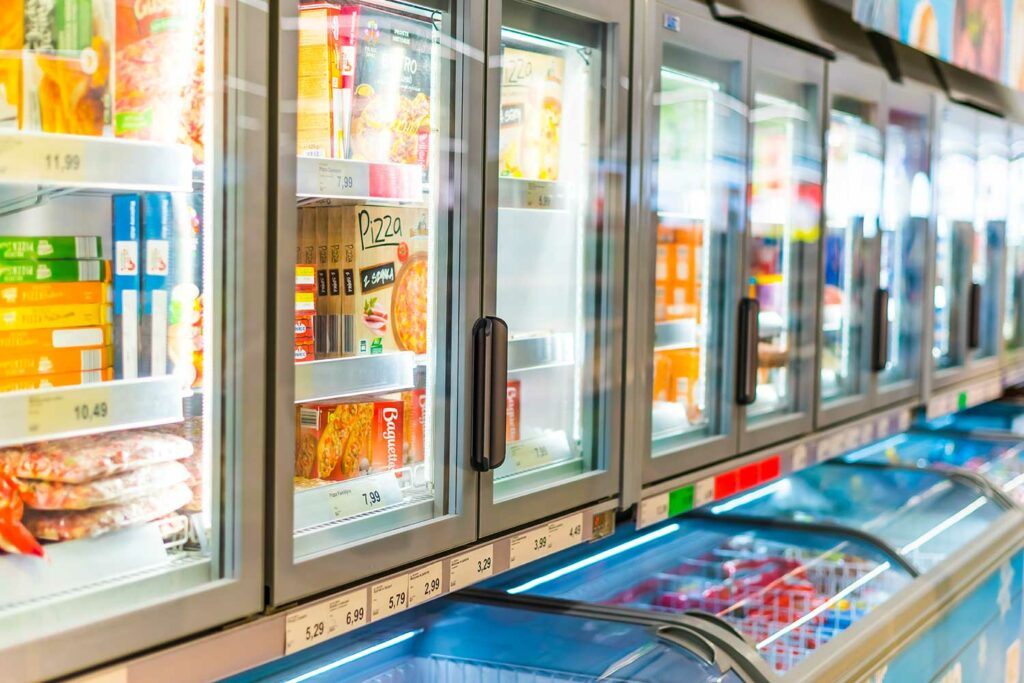

Convenience and Quality
The introduction of frozen foods revolutionized the way we eat and even how we commercialize foods.
In recent years, we’ve witnessed a growth in consumer demand for frozen foods for numerous reasons, such as:
- Convenience – Frozen food eliminates many of the hassles associated with food preparation, such as cleaning, chopping, and filleting.
- Longer Shelf Life – Buying frozen food means you can store it at home to consume at a later date. This means fewer trips to the grocery store and less waste.
- Healthy Options – Time constraints due to work and childcare mean many families don’t have time to buy and prepare fresh vegetables and fruit. Frozen veggies and fruits are a healthy, convenient option in these situations.
- Supports Global Commerce – Freezing foods on-site allows growers and fishermen to sell their products abroad. Likewise, prepared frozen foods can be commercialized nationwide and globally. Consumers, on the other hand, gain access to their favorite foods all year-round.
- Cost-Effective Alternative – Frozen goods are often more affordable than fresh products, and because frozen foods offer the option of bulk buying, it makes them more accessible to large families.
Nevertheless, extreme temperature drops may cause your instruments to malfunction. For instance, extreme cold can also lead to components freezing, and since metal contracts with cold, moving parts are subject to greater load stress, thus increasing the likelihood of failure.
Technologies Involved in the Frozen Food Industry
There are different methods of transferring cold temperatures utilized in the industry, namely:
- Air-Blast Freezers – The most common type of freezer, air-blast freezers work by circulating frigid air to cool the food.
- Contact Freezers – As its name suggests, with this type of equipment, food freezes when it comes in contact with icy surfaces or by immersion in a cold liquid.
- Cryogenic Freezers – This technology relies on liquefied gases such as nitrogen or carbon dioxide to generate frigid temperatures.
All these technologies rely heavily on precision thermometers and moisture meters to ensure the correct processing, packaging, and transportation of frozen foods.

How Allometrics Calibration Services Help the Frozen Food Industry
In an industry such as frozen foods, precision is critical, whether for temperature control or volume measuring. Therefore, calibration must be an integral part of the manufacturing process to guarantee the quality of the food products, ensure their safety, minimize waste, and maximize production efficiency.
With more than 47 years of experience in the industry, Allometrics can help calibrate your equipment. Our services guarantee accuracy and reliability with NIST traceability.
At Allometrics, we can calibrate your:
- Thermometers
- Moisture meters
- Balances
- pH meters
- Freezers
- Cold storage
We also offer temperature mapping, microbial testing, and clean certification.
Contact us for more information on how Allometrics help you with all your calibration needs.